Past Tense vs. Present Perfect: 5 Key Differences
Learn the key differences between past tense vs present perfect, understand verb tense rules, and master usage through tips, examples, and FAQs.

Past Tense vs. Present Perfect: Key Vocabulary
Introduction – Why This Matters
Many English learners struggle with past tense vs present perfect. Both refer to actions in the past, but which one to use? In casual speech and in exams, choosing wrongly makes sentences sound awkward or grammatically incorrect.
In this guide, you will:
Understand exactly what each tense expresses
Learn verb tense rules for both
See many real examples
Try practice exercises
Get tips, tricks, “Did you know?” facts, and FAQs
See how Clapingo can help you master them
By the end, you’ll feel confidence choosing between “I went” and “I have gone.”
What Is Past Tense?
The past tense (also called the simple past) describes actions or states that happened and finished in the past.
Structure
Affirmative: subject + past verb
She walked to school.
Negative: subject + did not + base verb
He did not visit the museum.
Question: Did + subject + base verb?
Did you see that movie?
Use Cases
When the time is definite and over
I visited my grandparents last summer.
To list a sequence of events
He woke up, ate breakfast, and left.
To express a single past event
She called me at 8 pm.
Signal Words (Past Tense)
Some common words associated with the past tense:
yesterday, last week, last year, ago, in 2015, when I was a child, earlier, at that time
What Is Present Perfect?
The present perfect tense links the past with the present. It shows that the result or effect is relevant now.
Structure
Affirmative: subject + has/have + past participle
They have traveled widely.
Negative: subject + has/have not + past participle
I have not finished my homework.
Question: Has/Have + subject + past participle?
Have you eaten lunch?
Use Cases
For actions at unspecified times
I have seen that movie (some time in the past).
For experiences
She has visited Japan twice.
For actions continuing up to now
I have lived here for five years.
For recent actions whose effects carry on
He has just left.
Signal Words (Present Perfect)
Common adverbs with present perfect:
ever, never, already, yet, just, recently, since, for, so far, up to now
Past Tense vs Present Perfect: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Past Tense | Present Perfect |
|---|---|---|
| Time reference | Definite, finished time | No definite time, connected to now |
| Focus | When the action occurred | The result, experience, ongoing state |
| Duration | Usually complete | May continue or affect now |
| Signal words | yesterday, ago, last year | ever, never, already, yet, since, for |
| Example | I visited Rome in 2018. | I have been to Rome. |
Example Pairs
Wrong: I have seen him yesterday. → Right: I saw him yesterday.
Wrong: They went to Paris once. → Better: They have been to Paris once.
Deeper into Time Expressions
Understanding time expressions (time markers) is key to decide which tense to use.
Past Tense Markers
yesterday, last week, in 2010, ago, when I was a child, then
Present Perfect Markers
ever, never, already, yet, just, recently, since, for, so far, up to now
Examples
I lived in Mumbai in 2015 → past tense.
I have lived in Mumbai for five years → present perfect (ongoing).
She has already finished her task. → “already” signals present perfect.
I did that task yesterday. → “yesterday” signals past tense.
Mistakes Learners Commonly Make
Combining an exact time with present perfect
Wrong: I have done that yesterday.
Fix: I did that yesterday.
Using past tense for ongoing actions
Wrong: I lived in Chennai since 2012.
Fix: I have lived in Chennai since 2012.
Omitting the signal word
Wrong: I have eaten dinner. (ok)
But in contrast: I ate dinner yesterday.
Confusing “I have gone” and “I have been”
I have gone to France. means you are there now (you went and you’re there).
I have been to France. means you visited at some time (you have returned).
Tips & Tricks to Choose the Right Tense
Tip 1: Ask: “Do I care when this happened?”
If yes → use past tense.
If no → use present perfect.
Tip 2: Look for time markers.
Tip 3: Use experience verbs (ever, never) with present perfect.
Tip 4: For actions that started before now and still continue, use present perfect.
Tip 5: Practice by labeling your own daily events in both tenses (journal).
Did You Know?
In British English, speakers often prefer present perfect where Americans use past tense. For example:
UK: Have you eaten yet?
US: Did you eat yet?
Some verbs rarely appear in the present perfect (e.g., arrive, appear, die) — so past tense is common.
The difference is subtle but changes meaning: “I lived in Delhi” (past) vs “I have lived in Delhi” (implies you might still live there).
Real-Life Examples and Mini Dialogues
Past Tense Examples
I watched the match yesterday.
She traveled last summer.
They bought a new car in 2018.
Present Perfect Examples
I have watched that match before.
She has traveled to many countries.
They have bought a new car recently.
Mini Dialogue
A: “Did you see that movie last night?”
B: “Yes, I saw it. But I have watched it before too.”
This shows both tenses naturally in one conversation.
Practice Exercises
Fill in the blanks with past tense or present perfect:
I ____ (visit) Berlin last year.
She ____ (travel) to Spain twice.
We ____ (finish) our homework already.
He ____ (not call) me yet.
They ____ (live) here since 2019.
I ____ (meet) him yesterday.
She ____ (work) for that firm for ten years.
You ____ (ever / go) to Canada?
Answers:
visited
has traveled
have finished
has not called
have lived
met
has worked
Have you ever gone
Clapingo Spoken English Sessions With Expert
Clapingo Section – Why Learning by Doing Helps
You can read grammar rules all day, but real improvement comes when you use those rules. That’s where Clapingo shines.
How Clapingo Helps
Live speaking sessions: You use tenses in conversation, not just in drills.
Instant feedback: Tutors correct your mistakes in real time.
Customized lessons: Focus on tenses you struggle with.
Everyday contexts: Use past tense vs present perfect in emails, reports, stories.
Clapingo Tip for Tenses
Ask your tutor: “If I say ‘I have done X’ vs ‘I did X,’ which is more natural here?” get direct comparison in real conversation.
Advanced Concepts & Related Tenses
Present Perfect Continuous
Use when an action started in the past and continues or recently stopped:
I have been reading for two hours.
Past Perfect
Use when one past action occurred before another:
By the time she arrived, I had already left.
Interaction of Tenses
Sometimes you combine:
I had lived in Delhi before I moved to Mumbai.
I have lived in Mumbai since 2020, and I have been working here since January.
Understanding all tenses gives you flexibility in expression.
More Tips & Tricks
✅ Anchor with dates: If you mention a date, go past tense.
✅ Use “yet” only with present perfect for negatives & questions: haven’t / hasn’t … yet?
✅ Never mix exact time + present perfect: “I have done it at 5 pm.” is incorrect.
✅ Short forms are common in speech: I’ve been, she’s done.
✅ Maintain consistency in longer writing: Don’t switch tenses unhelpfully.
Commonly Misused Verbs with Present Perfect
Certain verbs are often misused in the present perfect tense. Knowing these can help you avoid embarrassing mistakes.
Common verbs:arrive, die, happen, appear, start, finish, leave
Examples:
❌ Wrong: I have died last year.
✅ Correct: He died last year.
❌ Wrong: The concert has started yesterday.
✅ Correct: The concert started yesterday.
Tip: Use past tense when there’s a finished time, and present perfect only for experience or ongoing effects.
Fun Tense Quiz for Readers
Test your knowledge! Fill in the blanks with past tense or present perfect:
I ____ (see) that movie yesterday.
She ____ (travel) to Spain three times.
We ____ (finish) our homework already.
He ____ (not call) me yet.
They ____ (live) here since 2019.
Answer Key:
saw
has traveled
have finished
has not called
have lived
Share your score with friends or discuss it in a Clapingo session for live feedback!
Storytelling With Tenses
Changing tenses changes the tone of your story:
Past Tense Story:
Yesterday, I went to the park. I saw kids playing football and people jogging. It was a sunny day.
Present Perfect Story:
I have visited the park many times this month. I have seen kids playing football and people jogging there almost every day.
Lesson: Past tense = narrative feel; Present perfect = experience or ongoing observation.
Real Conversations: Past vs Present Perfect
Travel Scenario:
A: “Did you visit Paris last summer?”
B: “Yes, I visited the Eiffel Tower. I have also been to Versailles.”
Workplace Scenario:
A: “Did you finish the report yesterday?”
B: “Yes, I finished it. I have submitted it to the manager too.”
Tip: Reading dialogues aloud helps you internalize tense usage.
Common Signal Words Memory Tricks
Memorizing signal words helps you automatically choose the correct tense.
Mnemonic:
Past tense → YALAA → Yesterday, Ago, Last year, At that time
Present perfect → JEASY → Just, Ever, Already, Since, Yet
Clapingo Tip: Repeat aloud when writing or speaking for faster recall.
Errors That Change Meaning
Using the wrong tense can change meaning:
❌ I have met him yesterday. → Wrong
✅ I met him yesterday. → Correct
❌ I went to Paris once. → Ambiguous
✅ I have been to Paris once. → Correct and clear
Clapingo Lesson: Always check if you are stating a fact about the past or talking about experience/ongoing relevance.
Clapingo Spotlight: Live Correction Example
Example session transcript:
Student: “I have saw that movie yesterday.”
Tutor: “Remember, yesterday = past tense. Correct: ‘I saw that movie yesterday.’”
Lesson: Immediate corrections during live conversation reinforce learning faster than self-study.
Book a session to experience live grammar correction
Roleplay Scenarios
Travel:
Tutor: “Have you ever been to Paris?”
Student: “Yes, I have been there twice.”
Workplace:
Colleague: “Did you finish the report yesterday?”
You: “Yes, I finished it yesterday, and I have submitted it.”
Clapingo Tip: Practicing in scenarios makes tense usage automatic in daily speech.

Past Tense vs Present Perfect Tense in Everyday Conversations
Idioms & Expressions That Use Present Perfect
Examples:
I’ve been there before. → talking about experience
She has come a long way. → progress over time
We’ve had enough of this issue. → result affects present
Clapingo Lesson: Idioms often naturally require present perfect.
How Tenses Affect Storytelling Tone
Past tense = narrative, past events
Present perfect = reflective, ongoing, or experiential tone
Example:
Past tense: I traveled to Japan in 2019.
Present perfect: I have traveled to Japan several times.
Clapingo Lesson: Choose tense according to the mood you want to convey.
Workplace English: Tense Usage
Emails & Reports:
Past tense: We completed the task yesterday.
Present perfect: We have completed the task, so it’s ready for review.
Meetings:
I have finished the presentation. → emphasizes readiness now
I finished the presentation yesterday. → emphasizes when it happened
Clapingo Tip: Using correct tense boosts professional credibility.
Mistakes in Popular Media
Even movies and news sometimes mix tenses incorrectly:
“I have met him yesterday!” → often used in casual speech but grammatically incorrect
Correct: “I met him yesterday.”
Clapingo Lesson: Spotting mistakes in media makes learners more aware and sharp.
ESL Learner Success Stories
Example 1:
A student struggled with “I have saw” vs “I saw.” After 4 weeks of Clapingo sessions, she mastered correct usage in speaking and writing.
Example 2:
A professional improved workplace emails using past vs present perfect in meetings and reports.
Clapingo Lesson: Real-world practice accelerates learning.
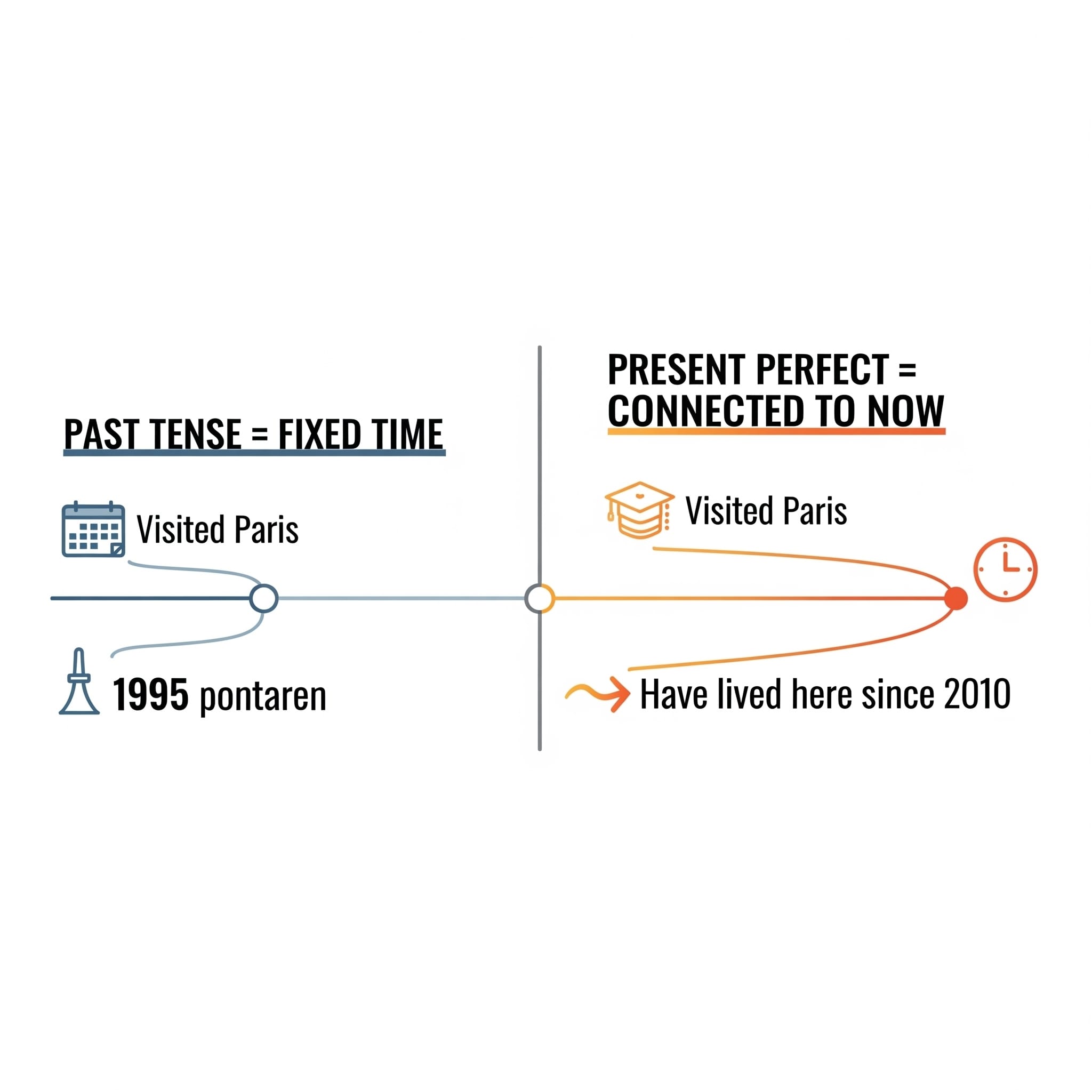
English Tense Correct Usage
Cheat Sheet: Quick Reference Table
| Feature | Past Tense | Present Perfect | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Specific, finished | Unspecified, ongoing | I went yesterday / I have gone several times |
| Focus | When | Experience / Result | I saw him yesterday / I have seen him before |
| Signal Words | yesterday, last year, ago | ever, never, already, yet, since, for | I met her last week / I have met her many times |
Clapingo Tip: Save or print this for quick reference while practicing.
Challenge Section: 7-Day Tense Challenge
Day 1: Write 5 sentences in past tense
Day 2: Write 5 sentences in present perfect
Day 3: Speak about your day using both tenses
Day 4: Record yourself narrating a story
Day 5: Correct your own sentences
Day 6: Practice with a friend or Clapingo tutor
Day 7: Review and track improvements
Share your challenge progress in a Clapingo session for feedback.
Story Time: Using Past Tense & Present Perfect Tense
A Weekend Adventure
Yesterday, I went to the mountains with my friends. We woke up early, packed our bags, and drove for three hours. The weather was perfect, and the air felt fresh. We hiked to a beautiful waterfall and took lots of photos.
Since then, I have shared the photos with my family and friends. I have received many messages saying how amazing the place looks. I have also planned another trip next month because I have enjoyed this one so much.
✅ Past tense examples: went, woke, packed, drove, was, felt, hiked, took (specific past events)
✅ Present perfect examples: have shared, have received, have planned, have enjoyed (actions connected to the present or experience)
The Surprise Birthday Trip
Last Saturday, my friends surprised me with a birthday trip. I woke up thinking it would be a normal weekend, but they had planned something special. They picked me up early in the morning, and we drove to a nearby lake. The sun was shining, and the birds were singing.
When we arrived, I could not believe my eyes. They had decorated a small cabin with balloons and banners. My best friend said, “We have prepared everything for your birthday!” I laughed and said, “Wow! I have never had such a surprise before!”
We spent the day swimming, playing games, and eating delicious food. I have already taken dozens of photos, and I have shared them on social media. Everyone has commented on how fun it looked.
By evening, we sat around a campfire. I told my friends, “I have always wanted a birthday like this, and now I have finally had one!” They smiled and said, “We’re glad you have enjoyed it.”
As we drove back home, I felt grateful. This trip has left me with memories that I will never forget.
✅ Past tense examples: surprised, woke, picked, drove, was, were singing, arrived, could not believe, laughed, spent, sat, told, felt, drove
✅ Present perfect examples: have prepared, have never had, have already taken, have shared, has commented, have always wanted, have finally had, have enjoyed, has left, will never forget
Conclusion
In the debate past tense vs present perfect, the difference lies in time specificity and connection to now. Use past tense for actions complete in the past with time labels. Use present perfect for experiences, ongoing states, or past actions that influence the present.
Mastering these rules boosts your writing and speaking fluency in English. But grammar rules alone don’t guarantee mastery. You need practice — especially in speech and real writing. And that’s where Clapingo comes in: you apply what you learn, get feedback, and improve fast.
If you found this guide useful, you can:
Try the exercises above
Share with learners who struggle with tenses
Book a trial session on Clapingo to practice one-on-one
Read Also:
Lingering Moments: A Deep Dive into Past Continuous Tense
Crafting Engaging Sentences: Mastering the Structure of Present Continuous Tense
Comments
Your comment has been submitted