Passed vs. Past: Grammar Rules, Meaning, and Usage Explained
Confused between “passed” and “past”? Learn the difference, grammar rules, examples, and tips to master usage. Includes past meaning, verb vs noun/adjective explanation, and ESL-friendly hacks.
Passed vs Past - What's the difference?
English learners often get confused between passed and past. The two words look and sound similar, but they have very different roles in grammar. One acts as a verb, while the other can be a noun, adjective, adverb, or even a preposition.
If you’ve ever hesitated while writing a sentence like “I passed by his house” or “I walked past his house”, you’re not alone. In this guide, we’ll break down the difference step by step so you’ll never mix them up again.
This blog will cover:
The difference between passed and past
Grammar rules with clear examples
Verb vs. noun/adjective usage explained
Common mistakes learners make
Tips, tricks, and memory hacks
Real-life practice examples
FAQs and Clapingo insights
By the end, you’ll confidently know when to use “passed” and when to use “past.”
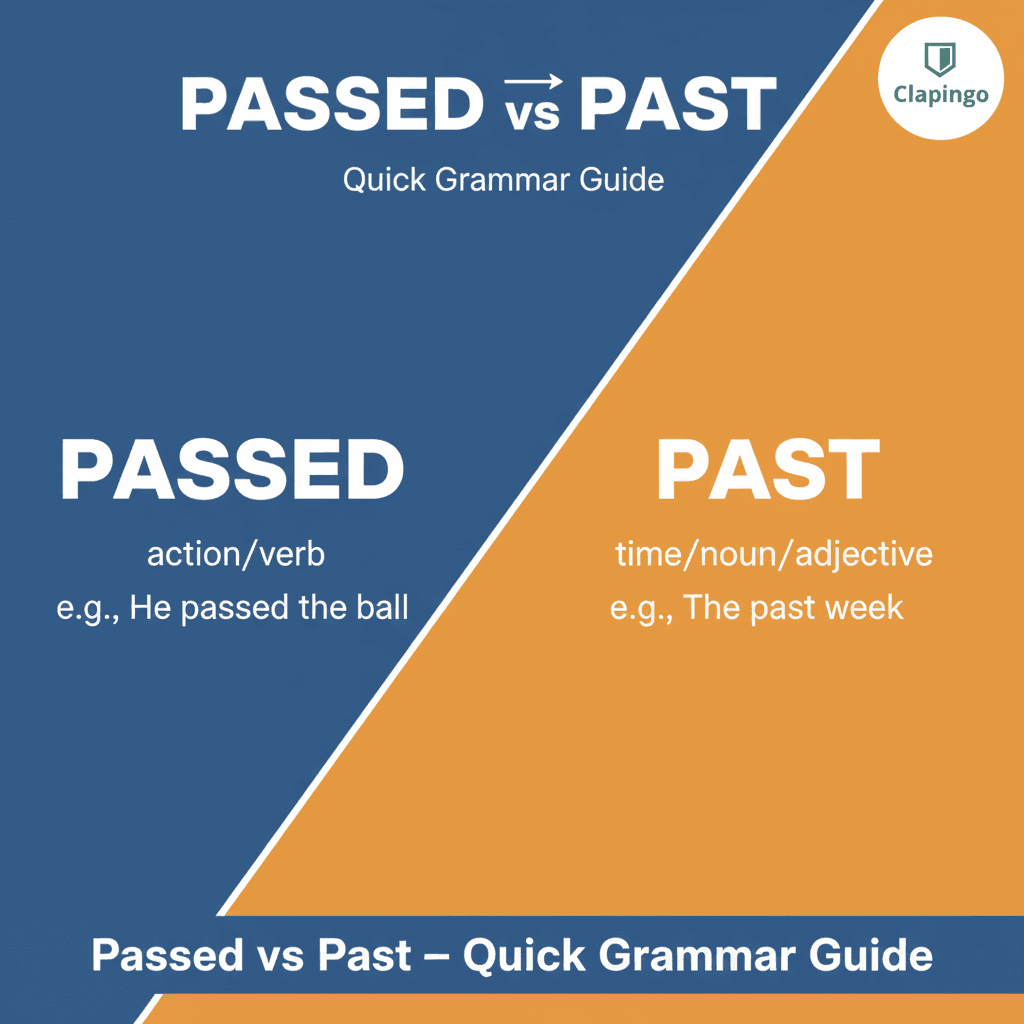
The Core Difference — Passed vs. Past
Let’s start simple.
Passed = Verb (action word) → Something happened or moved.
Past = Noun, Adjective, Adverb, Preposition → Refers to time, position, or description.
Quick Check:
If you’re describing an action, use passed.
If you’re describing time or position, use past.
Examples:
✅ I passed the exam. (Action → Verb)
✅ That is in the past. (Time → Noun)
✅ He walked past the shop. (Position → Preposition)
✅ She is past her deadline. (Stage → Adjective)
Meaning of Past (Noun, Adjective, Adverb, Preposition)
The word past is more flexible than “passed.” It can play many roles.
1. Past as a Noun
Refers to a time that has already happened.
You cannot change the past.
His past is full of surprises.
2. Past as an Adjective
Describes something related to an earlier time.
Past experience taught me well.
The past week was hectic.
3. Past as an Adverb
Indicates movement beyond a point.
He ran past quickly.
4. Past as a Preposition
Shows movement or position.
I walked past the station.
She drove past my house.
Passed Meaning and Usage (Verb)
The word passed is only the past tense of the verb “pass.”
It means to move, succeed, hand over, or go beyond.
Uses of “Passed”
1. Movement
I passed the ball to her.
The car passed me on the highway.
2. Success
She passed the exam.
I finally passed my driving test.
3. Time Passing
Three hours passed quickly.
4. Death (polite use)
He passed away last year.
Always remember: Passed = action (verb).

Passed vs Past - Grammar Differences
Grammar Rules (Verb vs. Noun/Adjective)
This is where learners get stuck. Let’s make it easy.
If the sentence needs a verb (action word) → Use passed.
If the sentence needs a noun/adjective/adverb/preposition (time/position/description) → Use past.
Rule Table
Function | Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
Verb | Passed | She passed the note. |
Noun | Past | We should forget the past. |
Adjective | Past | I learned from past mistakes. |
Adverb | Past | He walked past quickly. |
Preposition | Past | The train went past the bridge. |
Common Mistakes Learners Make
❌ I past the exam.
✅ I passed the exam.❌ She walked passed the shop.
✅ She walked past the shop.❌ Let’s forget about the passed.
✅ Let’s forget about the past.
Clapingo Tip: If you’re describing an action, use “passed.” If you’re talking about time or position, use “past.”
Clapingo tutors help you use words like passed and past correctly — without translating in your head.
Tips and Tricks to Remember the Difference
Memory Hack 1: Passed ends with “-ed” → just like other past tense verbs.
Memory Hack 2: Past = Time/Position → Think “timeline” or “location.”
Memory Hack 3: Replace the word with “went by.” If it works, use “passed.”
The car went by quickly → works → use “passed.”
That is in the went by → doesn’t work → use “past.”
Did You Know?
“Past” comes from the Latin praeter, meaning “beyond.”
“Passed” only appeared after English adopted “-ed” endings for verbs.
Many native speakers also confuse them—so you’re not alone!
Practice Sentences
Fill in the blanks with passed or past.
She _______ the ball to me.
Let’s move on from the _______.
He walked _______ my house yesterday.
I _______ the test after studying hard.
The deadline is already _______.
Answers: 1) passed, 2) past, 3) past, 4) passed, 5) past
Clapingo Corner – Learn the Difference in Conversation
At Clapingo, we help learners master confusing English words like “passed vs. past” through live 1-on-1 practice with expert tutors.
Imagine a conversation:
You say: “I past my exam.”
Tutor corrects: “It should be ‘passed’ because you’re talking about an action.”
You practice with examples until it becomes natural.
Clapingo makes grammar practical, not boring.
Start practicing with Clapingo today
Take your first Clapingo demo class and feel the difference.
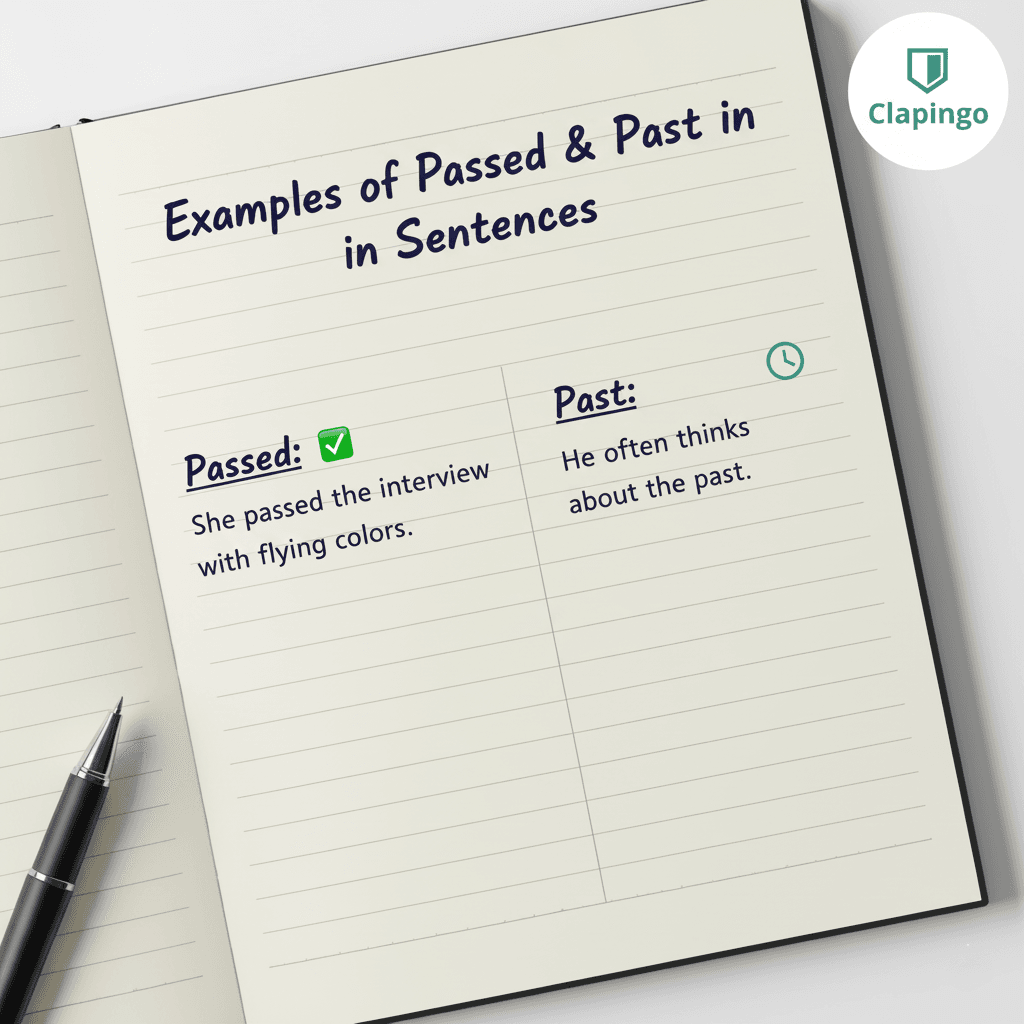
Real-Life Usage Examples
✅ The bus passed on time. (Verb)
✅ The bus stop is just past the market. (Preposition)
✅ He learned from past experiences. (Adjective)
✅ Time passed so quickly during the trip. (Verb)
✅ She walked past me without noticing. (Adverb)
Examples of Passed vs Past
Idiomatic Expressions with Past
Learning idioms with past is a great way to sound more natural in English. Here are some common expressions:
Let bygones be bygones – Forgive past conflicts and move on.
Example:They had a fight last year, but they decided to let bygones be bygones.
A thing of the past – Something that no longer exists or is no longer relevant.
Example:Using fax machines is a thing of the past.
Past your prime – Beyond your best years.
Example:He’s past his prime, but he still enjoys playing football.
Learn from the past – Take lessons from previous experiences.
Example:She learned from the past mistakes and never repeated them.
Tip: Try to use one idiom in a sentence every day to remember it better.
Common Collocations with Passed
Certain words naturally pair with passed. Learning these collocations helps you speak and write more fluently:
Passed away – Passed on; died.
Example:Her grandfather passed away last night.
Passed out – Fainted or lost consciousness.
Example:He passed out from exhaustion.
Passed the test/exam – Succeeded in a test or challenge.
Example:She passed the driving test on her first try.
Passed by – Moved past something.
Example:I passed by your office yesterday, but you weren’t there.
Tip: Pair the verb pass with different prepositions to create multiple meanings. It’s a small change but changes the meaning entirely.
How to Avoid Confusing Similar Words
Even advanced learners sometimes confuse similar words. Here’s how to avoid mixing up passed and past:
Identify if the word is an action or a description.
Action → passed
Description/time/position → past
Test the sentence with the word “went by.”
I passed the shop. → Works → passed
That is in the went by. → Doesn’t work → past
Watch for prepositions: past often follows nouns (e.g., walked past the park).
Clapingo Pro Tip: When in doubt, ask yourself: Am I talking about something that happened (verb) or something related to time/position (noun/adjective)?
At Clapingo, every session helps you use words like passed and past naturally in daily life.
Past Tense vs. Past Participle Confusion
Passed is both the past tense and past participle of the verb “pass.” Many learners get confused between simple past and present perfect.
Past Tense (action completed in the past)
I passed the exam yesterday.
Present Perfect (action completed with a connection to the present)
I have passed the exam, so I can celebrate now.
Past participle trick: If the sentence has have/has/had, it’s likely a past participle.
She has passed all her courses.
Clapingo Pro Tip: Remember: past tense = simple action; past participle = action linked to now or another past event.
Phrases to Practice in Daily Conversation
Practical phrases help you internalize the difference between passed and past:
I passed by the store on my way home. → Action (verb)
That’s all in the past now. → Time (noun)
He passed the baton to his teammate. → Action (verb)
You can’t undo the past. → Time (noun)
I walked past your office yesterday. → Position (preposition)
Clapingo Pro Tip: Keep a small notebook and write down two sentences per day using passed and past. Over a week, you’ll see rapid improvement.
Simple Trick - Passed vs Past
Visual Trick to Remember the Difference
Visual learners can benefit from a simple timeline trick:
Past → Timeline Marker → Points to a moment or period in time.
Passed → Moving Object → Shows action or something that has happened.
Example:
Past (noun/adjective) → 2010, 2015, last week
Passed (verb) → I passed the exam → action moving along the timeline
Exercise: Draw your own timeline for the last week. Label actions with passed and periods with past.
Quiz Yourself – Mini Challenge
Fill in the blanks with passed or past:
She ______ her driving test last month.
Time flew by; it’s already in the ______.
He walked ______ my house yesterday.
That problem belongs to the ______.
I ______ the bakery on my way to work.
Answers: 1) passed, 2) past, 3) past, 4) past, 5) passed
Clapingo Tip: Repeat this exercise daily with your own sentences. Writing helps retention more than just reading.
Real-Life Examples from Literature & Media
Seeing examples in books, movies, or articles makes learning easier.
“Those were the best days of my past.” → Noun usage
“He passed the castle without noticing it.” → Verb usage
“Time passed quickly as they talked.” → Verb usage
“Walk past the museum to reach the park.” → Preposition usage
Clapingo Tip: Highlight any sentences you see in your reading with passed or past. Write them down and say them aloud.
Common ESL Mistakes and How to Correct Them
Even after learning rules, mistakes happen. Here are common pitfalls:
❌ I past the exam. → Confusing verb vs noun
✅ I passed the exam.❌ She walked passed the shop. → Overusing “-ed”
✅ She walked past the shop.❌ Let’s forget about the passed. → Using verb as noun
✅ Let’s forget about the past.
Clapingo Pro Tip: Reading your sentence aloud often reveals if it “sounds right.” If it sounds off, check passed vs past.
Common Exam Mistakes with Passed vs. Past
Students often mix these words in tests and assignments. Here’s how to avoid it:
❌ I past my math exam. → Wrong, verb needed
✅ I passed my math exam.❌ All our mistakes are in the passed. → Wrong, noun needed
✅ All our mistakes are in the past.❌ He ran past the finish line successfully. → Correct! This is a preposition, not a verb mistake
Clapingo Tip: Always ask: “Am I describing an action or a time/position?” If it’s an action → passed; if it’s time/position → past.
Join a Clapingo demo session and fix common grammar errors instantly.
Fun Memory Tricks for ESL Learners
Making learning fun helps retention. Here are some tricks:
Visualize a race track:Passed = runner moving → action; Past = timeline mark → time.
“-ed” rule: Most verbs in past tense end with “-ed.” So if it ends with “-ed,” it’s likely an action.
Replace with “went by”: Works? → passed; doesn’t work? → past.
Create mini-stories:
Yesterday, I passed the bakery. It reminded me of past birthdays. → Action + Time
Clapingo Tip: Draw simple doodles or timelines for every sentence you write with passed or past. Visual learning sticks better.
How Professionals Use Passed vs. Past
Even in business emails and corporate communication, using the correct word matters:
Passed (verb):
I passed the client’s report to the team for review.
The proposal passed the compliance check.
Past (noun/adjective/preposition):
Let’s learn from past project delays.
We walked past the new office during the site visit.
All deadlines in the past quarter have been reviewed.
Clapingo Pro Tip: When writing professional emails, reread sentences and check if the word describes an action (passed) or time/position/description (past). This small check can prevent embarrassing mistakes.
Clapingo Spotlight – Interactive Learning Hacks
At Clapingo, learners practice tricky words like passed and past in interactive and memorable ways:
Role-play: “Describe what happened in the past month.”
Real-time corrections: Tutors instantly fix sentences like “I past the exam” → “I passed the exam.”
Speed drills: Identify and choose correct usage under time pressure.
Storytelling: Create stories using both passed and past.
Benefit: You don’t just memorize rules; you practice in real conversation contexts, so the correct usage becomes natural.
Final Thoughts
The difference between passed vs. past comes down to grammar roles:
Passed = Verb (action)
Past = Noun, Adjective, Adverb, Preposition (time, position, description)
Once you get this simple rule, you’ll never confuse them again.
Want to master such tricky English pairs?
Clapingo offers personalized practice with native-level tutors who help you sound fluent and confident in real conversations.
Take your English to the next level with Clapingo
Practice them aloud with real feedback.
Join a 1-on-1 Clapingo demo and see your grammar confidence soar.
Read Also: Either vs Neither: Understanding the Choice and Negation
Comments
Your comment has been submitted