Has vs. Have: What’s the difference? Is it just tenses?
Confused between “has” and “have”? Learn the difference between has and have, grammar rules, usage tips, subject-verb agreement, and examples to master English fluency.

English Learner confused with Grammar Concepts
English grammar can feel overwhelming, especially when two simple words “has” and “have” seem to do the same job. Knowing when to use “has” and “have” makes all the difference while sounding fluent and professional.
In this article, we’ll break down the difference between has and have, highlight grammar rules, give real-world examples and offer simple hacks to avoid common mistakes.
What’s the Basic Difference Between Has and Have?
Let’s start at the beginning. Both “has” and “have” are forms of the verb “to have,” which shows possession, experience or a relationship.
Verb Tense Usage
Have Present Used with I, you, we, they, and plural nouns
Has Present Used with he, she, it, and singular nouns
Example:
I have a new phone. ✅
She has a new phone. ✅
The difference lies in the subject, who or what is doing the action.
When to Use Has and Have
Use “Have” With:
I
You
We
They
Plural nouns
Examples:
Ihavethree meetings today.
They havetwo children.
The players havefinished the match.
Use “Has” With:
He
She
It
Singular nouns
Examples:
He hasa big idea.
The dog hasa shiny coat.
My friend has a new car.
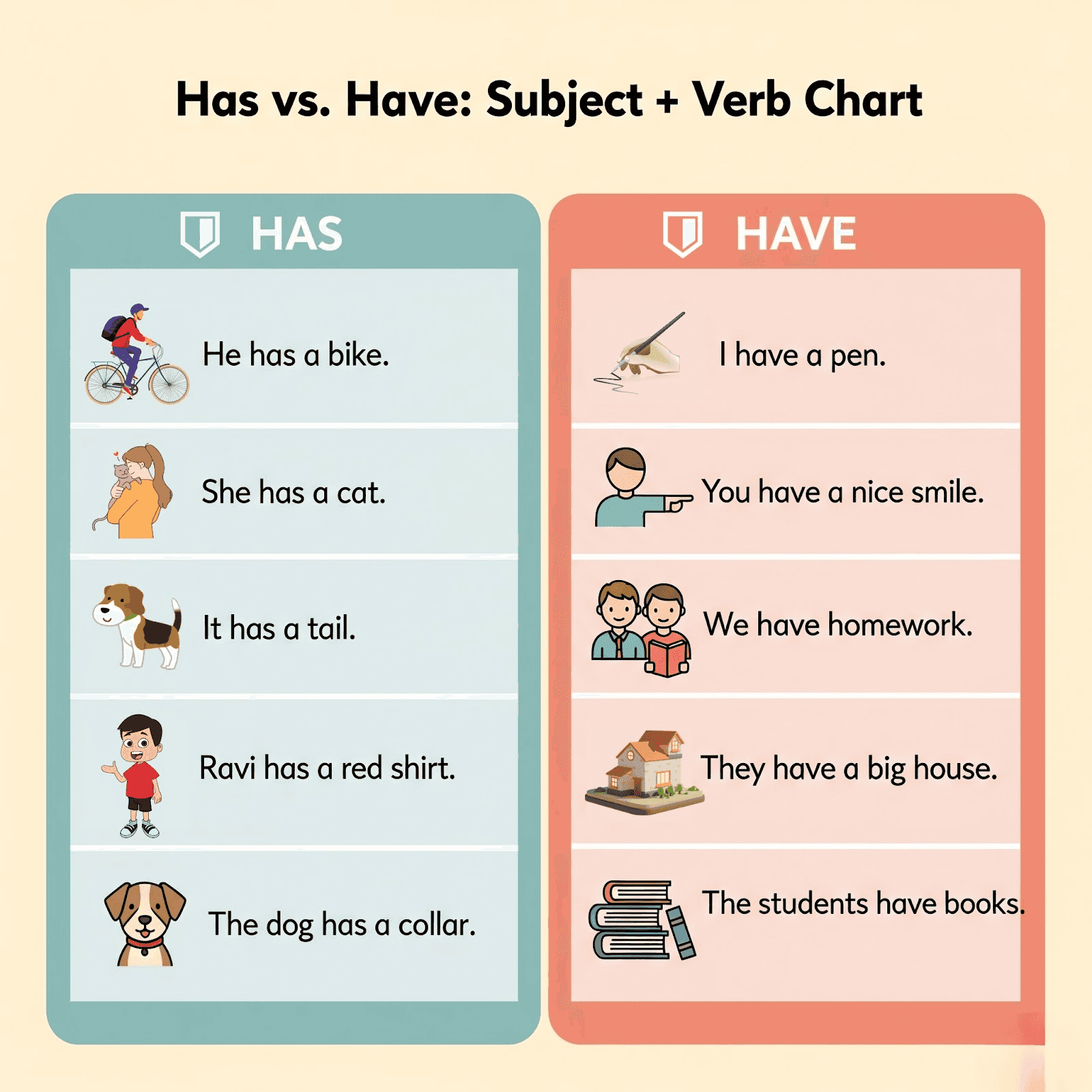
Has vs Have: Subject + has/have + Object Chart
Grammar Rules - Has and Have
Here are some key grammar rules to remember:
Rule 1: Subject-Verb Agreement
The verb must agree with the subject in number and person.
Singular subject → use has
Plural subject → use have
Rule 2: Questions and Negatives
When forming questions or negatives in the present perfect tense, use “have” or “has” with a past participle.
Examples:
Has she eaten breakfast?
They have not gone to the party.
Have you seen the email?
Rule 3: Possession vs. Action
“Have” and “has” can show ownership or can be helping verbs in perfect tenses.
Possession:
I have a pen.
She has two kids.
Action:
I have seen the movie.
He has worked here for 10 years.
Subject-Verb Agreement with Has/Have
Subject-verb agreement ensures your subject matches your verb in number and person.
Subject Type | Verb | Example |
First Person | Have | I have a cold. |
Second Person | Have | You have great taste. |
| Third Person | Has | She has a meeting today. |
Plural Subjects | Have | The kids have homework. |
Clapingo Quick Tip: If the subject ends in “s” (usually plural), it likely takes “have.” If the subject is a singular name or pronoun like “he” or “she,” it likely takes “has.”
Singular vs. Plural with Has/Have
Let’s take a closer look:
Subject | Singular/Plural | Use | Example |
My brother | Singular | Has | My brother has a car. |
My brothers | Plural | Have | My brothers have a car. |
The teacher | Singular | Has | The teacher has notes. |
The teachers | Plural | Have | The teachers have books. |
This is a common area of confusion. Always identify whether your subject is one or more than one.
Examples of Has and Have in Sentences
Have:
I have a flight at 6 p.m.
You have a lovely smile.
We have the same goals.
The employees have finished their tasks.
Has:
She has a busy schedule.
It has a strange smell.
Rahul has two sisters.
The phone has no battery left.
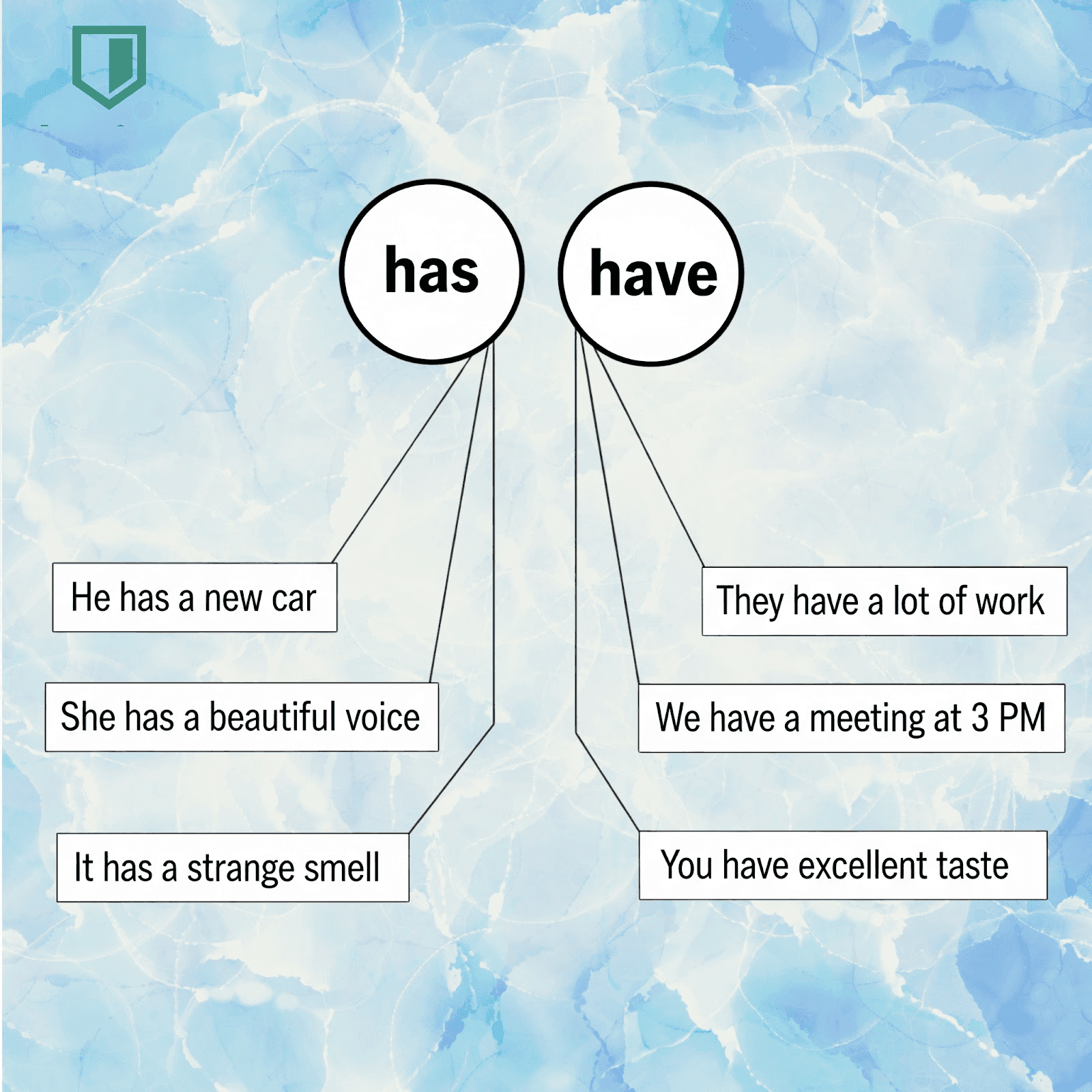
Has vs Have: Simple Examples
Common Mistakes with Has and Have
Mistake 1: Using “has” with “I” or “we”
Incorrect: I has a plan.
Correct: I have a plan.
Mistake 2: Using “have” with singular third-person
Incorrect: He have a dog.
Correct: He has a dog.
Mistake 3: Misunderstanding plural subjects
Incorrect: The group have arrived.
Correct: The group has arrived. (“group” is singular)
Have you checked out our blog? Choosing Right Verb Tense: A Guide to Simple Past and Present Perfect
Tips and Tricks to Master Has vs. Have
Tip 1: Memorize subject-verb pairs (He/She/It → Has; I/You/We/They → Have)
Tip 2: Practice speaking with a partner or mirror
Tip 3: Think of “has” as the fancier cousin used only in formal singular cases
Tip 4: Use flashcards or apps to reinforce examples
Tip 5: Read children’s books. They often use these forms clearly and repeatedly
“Did You Know?”
Some Fun Facts About English Verbs
The verb “have” is among the top 10 most used verbs in English.
“Have” is irregular, its past tense is “had,” which is the same for all subjects!
In older English, “hath” was used instead of “has.”

Trial Sessions With Clapingo Experts
Book a trial session on Clapingo now!
Learn with Clapingo: Practice Has and Have in Real Conversations
Want to get comfortable using “has” and “have” in your daily life? Practice with a real English expert on Clapingo, India’s leading spoken English platform.
- Speak with trained tutors
- Get feedback on your grammar in real-time
- Build confidence in using “have/has” naturally
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between has and have might seem like a small detail, but it has a big impact on how professional and fluent you sound. With the right grammar rules, subject-verb agreement and of course adequate practice, you’ll master these verbs in no time.
However, remember, learning English is easier when you practice with a real person. Join Clapingo and start building your fluency with expert tutors today!
FAQs
Q1: Can I use “have” with “he” or “she”?
No, use “has” with he, she, or it. Example: She has a headache.
Q2: Is it ever okay to say “he have”?
Only in informal or non-standard dialects. In standard English, it’s incorrect.
Q3: What about “has been” vs. “have been”?
“Has been” is used for singular third-person subjects.
“Have been” is used for I, you, we, they.
Q4: Why is this important?
Using the correct form improves clarity, fluency and confidence especially in job interviews or public speaking.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted